Glioma Markers
Monoclonal Antibodies from Atlas Antibodies
Gliomas are one of the most aggressive and lethal solid tumors of the central nervous system. Despite the alarming numbers, the molecular pathogenetic mechanisms of gliomas are not yet fully elucidated.
 Our partner Atlas Antibodies provides a portfolio of PrecisA Monoclonals targeting glioma TME markers for better distinction between different forms of glioma by IHC analysis.
Our partner Atlas Antibodies provides a portfolio of PrecisA Monoclonals targeting glioma TME markers for better distinction between different forms of glioma by IHC analysis.
Gliomas are solid tumors of the central nervous system (CNS), that arise from the neoplastic transformation of glial cells, namely astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and ependymal cells. The identification of molecular biomarkers is essential and urgent for an accurate prognosis and development of critical therapeutic targets in gliomas. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) plays a vital role in distinguishing between different tumor types. In gliomas neuropathological diagnostics, antibodies directed towards proteins such as IDH (isocitrate dehydrogenase), ATRX (alpha thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome X-linked), GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), SYN (synaptophysin), EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor), p53 (tumor suppressor protein 53), and the proliferation marker Ki-67 (MKI67) are the gold standard and routinely used.
Examples of IDH1, ATRX, and GFAP multiplexed IHC-IF staining in different glioma grades:
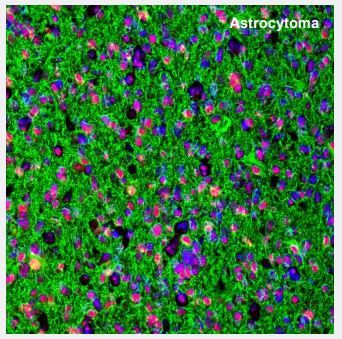 |
Figure 1. ATRX and GFAP in astrocytoma. Multiplexed IHC-IF staining of astrocytoma showing ATRX (nuclear, red) and GFAP (cytoplasmic, green) immunoreactivity in tumor cells. The Anti-ATRX antibody (AMAb90784) and Anti-GFAP antibody (AMAb91033) were used. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. |
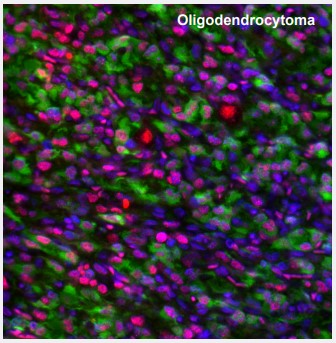 |
Figure 2. ATRX and IDH1 in oligodendrocytoma. Multiplexed IHC-IF staining of anaplastic oligodendroglioma showing ATRX (nuclear, red) and IDH1 (cytoplasmic, green) immunoreactivity in tumor cells. The Anti-ATRX antibody (AMAb90784) and Anti-IDH1 antibody (AMAb90578) were used, nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. |
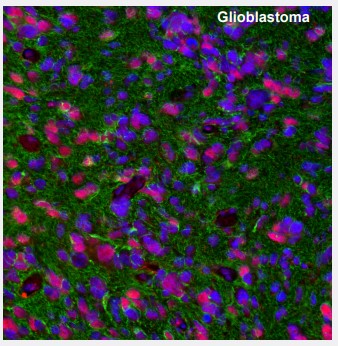 |
Figure 3. ATRX and GFAP in glioblastoma. Multiplexed IHC-IF staining of glioblastoma multiforme showing ATRX (nuclear, red) and GFAP (cytoplasmic, green) immunoreactivity in tumor cells. The Anti-ATRX antibody (AMAb90784) and Anti-GFAP antibody (AMAb91033) were used, nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. |
The glioma tumor microenvironment
The dynamic communication between tumor cells and the surrounding tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a crucial role in the sustained growth, proliferation, and invasion of gliomas, survival, evasion of cell death, metabolism, migration, and metastasis. Four mechanisms in the TME have emerged as paramount for our understanding of gliomas and crucial for the development of new treatment strategies: immunomodulation, angiogenesis, glioma cancer stem cells (GSC), and drug resistance. Targeting GSCs is an extremely important aspect of the clinical treatment of gliomas. A better comprehension of glioma GSCs provide functional insights into the dynamic of cellular communication during gliomagenesis, creating new opportunities for diagnostics and therapeutics.
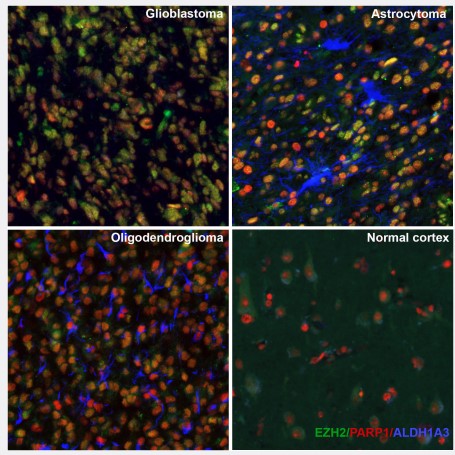
Figure 4. New TME markers. Multiplexed IHC-IF staining of human glioblastoma, astrocytoma, olygodendrocytoma and normal cortex samples using the Anti-EZH2 monoclonal (AMAb91752) (nuclear, in green), the Anti-PARP1 monoclonal (AMAb90959) (nuclear, in red) and the Anti-ALDH1A3 monoclonal (AMAb91754) (cytoplasmic, in blue) antibodies.
Selected PrecisA Monoclonals targeting glioma TME markers:
| Product Name | Target Protein | Biological Role in Gliomas | Validated Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-ALDH1A3 |
Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 | Marker for mesenchymal glioma phenotype | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-CHI3L1 |
Chitinase-3-like protein 1 | Carbohydrate-binding protein; Marker for invasion, migration and angiogenesis in glioblastoma | IHC, WB |
|
Anti-EZH2 |
Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit | Transcription factor; Marker for glioma stem cells | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-FOXM1 |
Forkhead box M1 | Transcriptional activator involved in cell proliferation; Marker for glioma progression | IHC, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-GLI1 |
GLI family zinc finger 1 | Cancer cell migration | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-ID1 |
Inhibitor of dna binding 1, hlh protein | Transcriptional regulator; Critical for glioblastoma initiation and chemoresistance | IHC, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-NF1 |
Neurofibromin 1 | Immunomodulation | ICC-IF |
|
Anti-PTEN |
Phosphatase and tensin homolog | Cell cycle progression and proliferation; Marker for mesenchymal phenotype | IHC, WB |
|
Anti-POSTN |
Periostin | Extracellular matrix protein; Cancer stem cell maintenance and metastasis | IHC, ICC-IF |
|
Anti-RBFOX3 |
RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3 | Transcription Factor; Marker for neural glyoma phenotype | IHC |
|
Anti-SALL4 |
Spalt like transcription factor 4 | Transcription factor; Maintenance and renewal of stem cells | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
This might also interest you
>> Scientific News: Neuroinflammation - Antibodies for western blot and immunohistochemistry
>> Scientific News: Amytracker fluorescent tracers - High-quality visualization of amyloids
>> Scientific News: Cancer Research - PathPlus™ validated antibodies from LSBio
>> Journal Club: Antibodies are valuable tools in clinical research - 3 case studies
26.01.2022

Cell Manipulation
MDR Approval for Medical Devices

Labortops #2
Super Sale: up to 88% off labware
Obesity and Metaboli...
Research Reagents from Rockland, GeneTex and more

Spring Promo
Up to 30 % off Antibodies and ELISA kits

Protein Expression
MoBiTec Cloning and Expression Vectors

