![]()
|
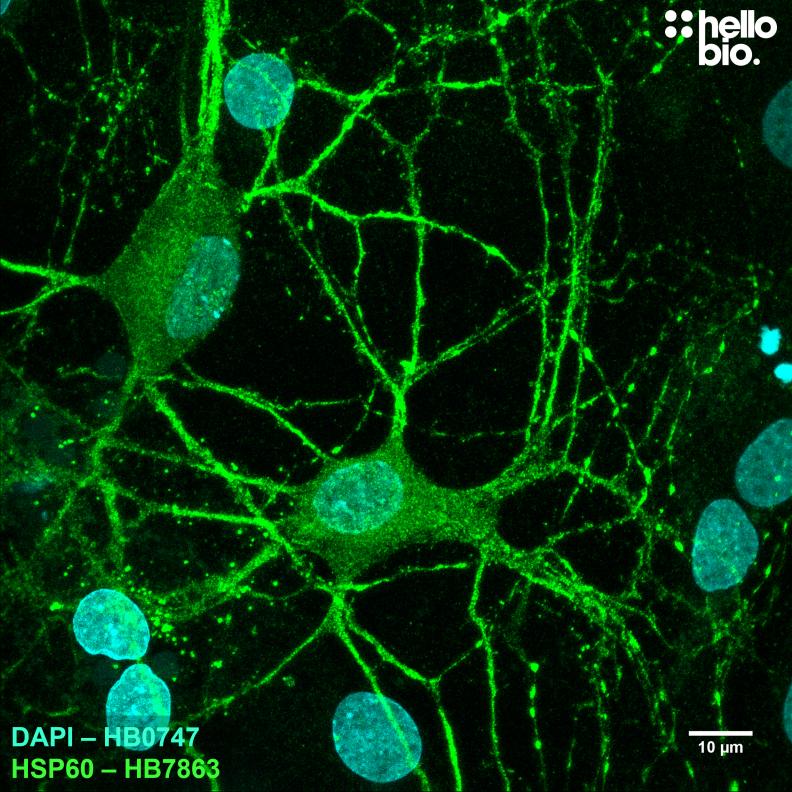
Figure 1. HSP60 staining with HB7863 reveals the dense mitochondria in cultured rat neurones. Mitochondria are highly prevalent in neurones due to their high energy requirements; this was visualised using HB7863 in cultured rat neurones. Method: neurones were cultured from PND2 rats following established protocols (Brewer and Torricelli, 2007. Nat Protoc 2, 1490–1498) and fixed with 4% PFA on DIV21. Cells were permeabilised with 0.1% Triton X-100 followed by blocking in 1% BSA, 300mM glycine. HB67863 was incubated overnight (4°C) at a 1:1000 dilution (1µg/ml) followed by a one hour incubation with secondary antibody (Polyclonal goat anti-mouse DyLight 488 conjugated, Thermofisher 35503, 1:300 dilution). DAPI (HB0747) was used at 1µg/ml to visualise cell nuclei. For more detail please see our ICC protocol. Images were captured using a Leica SPE confocal laser scanning microscope coupled to a Leica DMi8 inverted epifluorescence microscope. The image was captured using a 63x objective (1.41x zoom) and 405nm (43.5% power, gain: 658) / 488nm (36.8% power, gain: 881) laser lines in a z-stack (0.18 µm spacing). Deconvolution was carried out using Huygens Essential (Scientific Volume Imagine) followed by the stack being flattened using a maximum Z projection in ImageJ (Schindelin et al., 2012. Nat Methods, 9(7), 676–682). |
![]()
|
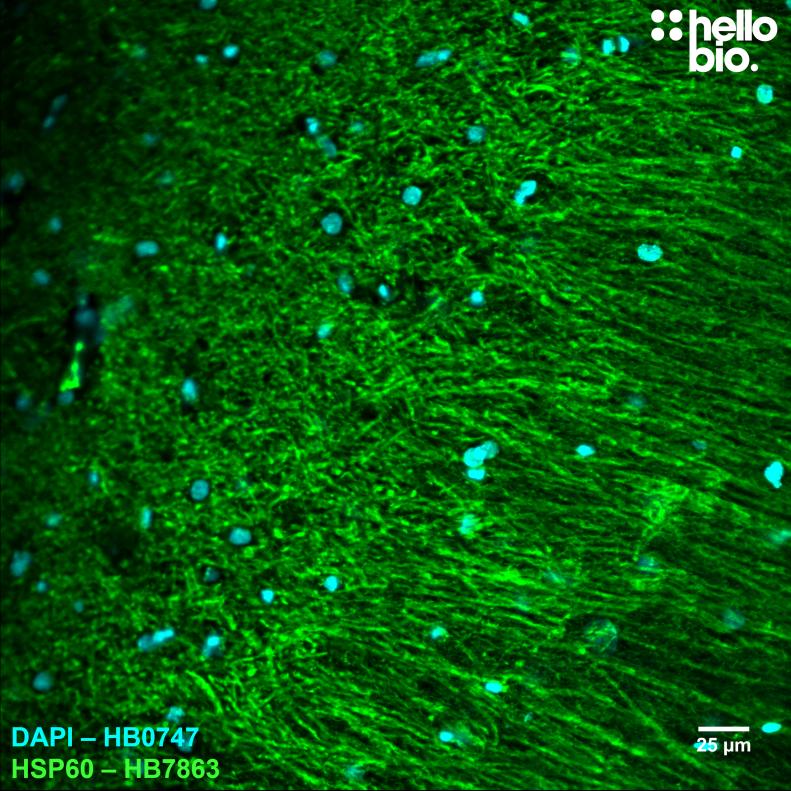
Figure 2. HSP60 expression in rat CA1 visualised using HB7863. HB7863 visualised the dense network of fibres present in the stratum radiatum and stratum lacunosum moleculare of rat CA1. Method: hippocampi were dissected from rat brains and fixed overnight in 4% PFA before then being incubated in 30% sucrose (in PBS) for another 24hrs. A freezing microtome was used to cut 40µm transverse slices before sections were incubated in 0.05M glycine for 30 minutes. Sections were blocked in 1% BSA, 22.52mg/ml glycine before incubation overnight in HB7863 (1:2,000 dilution, 0.5µg/ml). This was followed by a two hour incubation with secondary antibody (Polyclonal goat anti-mouse DyLight 488 conjugated, Thermofisher 35503, 1:300 dilution). DAPI (HB0747) was used at 1µg/ml to visualise cell nuclei. For more detail please see our IHC(IF) protocol. The image was captured using a Leica SPE confocal laser scanning microscope coupled to a Leica DMi8 inverted epifluorescence microscope. The image was captured using a 40x objective and 405 (20.0% power) / 488 (27.0% power) laser lines. The image was processed in ImageJ (Schindelin et al., 2012. Nat Methods, 9(7), 676–682). |
![]()
|
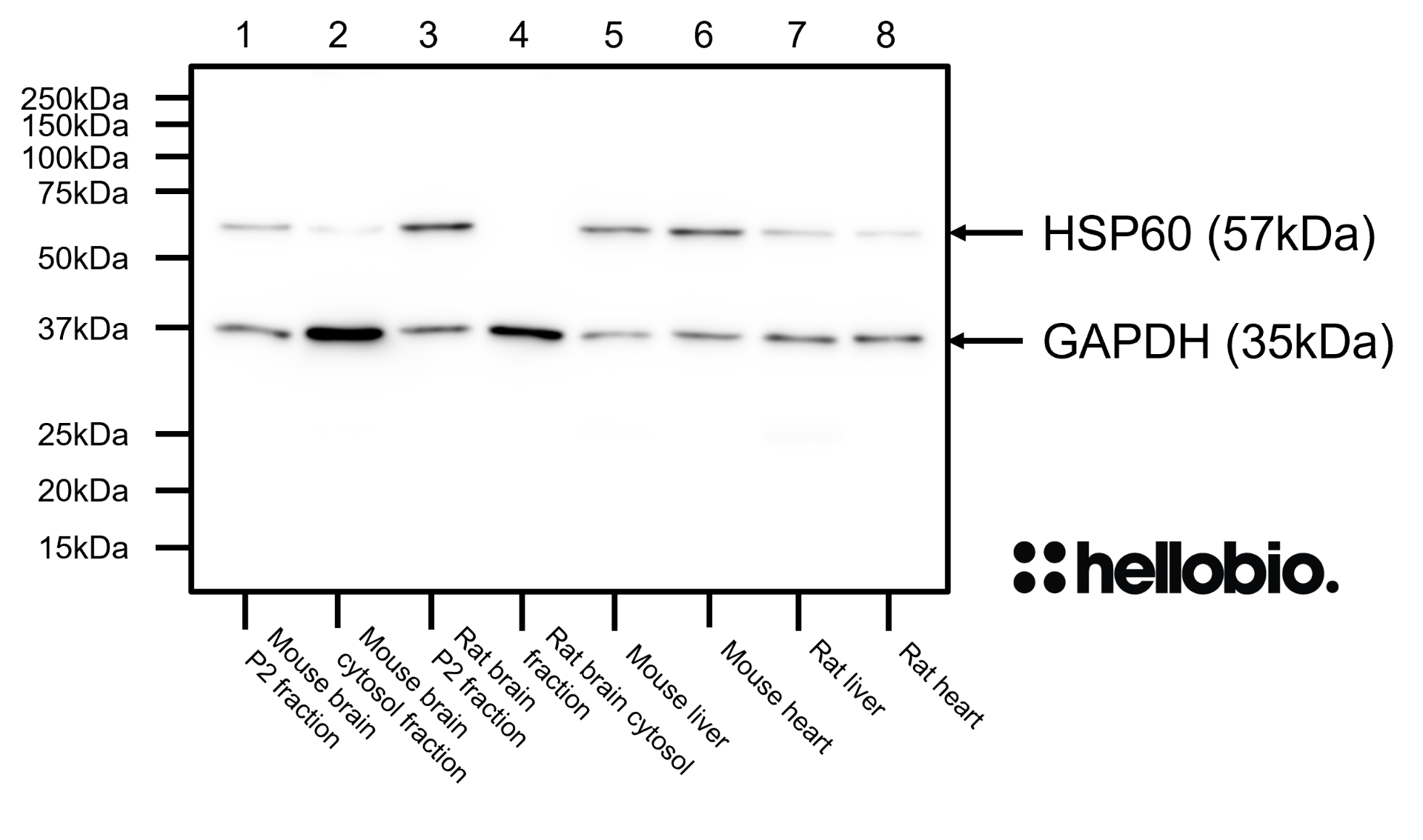
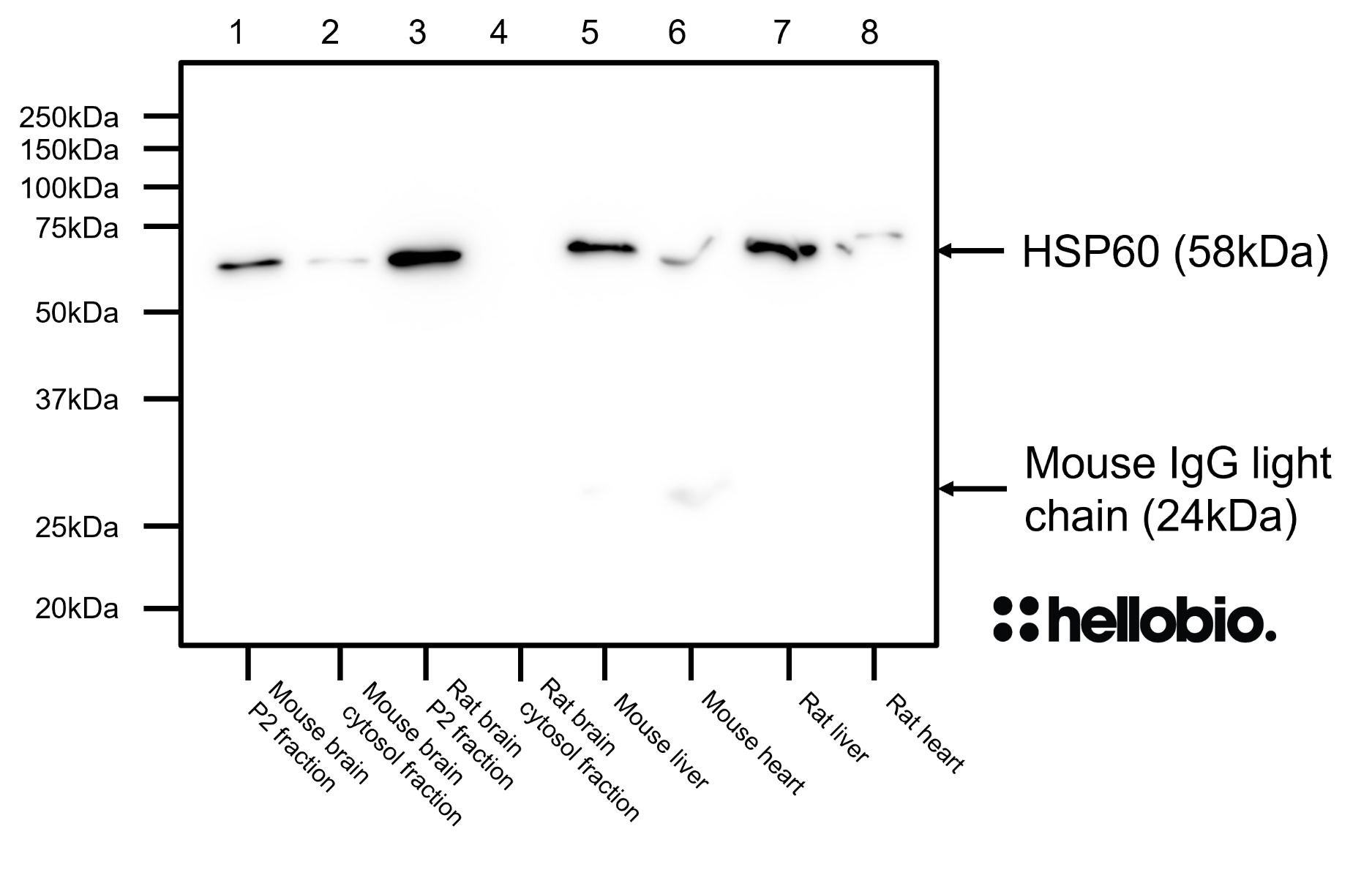
Figure 3. HSP60 expression in various tissue lysates and preparations. HB7863 revealed a single band of size 57kDa present in all samples except the rat brain cytosol fractions. Method: mouse brain and rat brain membrane (P2) and cytosol fractions were prepared following previous work (Molnar et al., 1993. Neuroscience 53:307-326) from freshly collected adult brains. Other tissue lysates were prepared following established protocols from freshly dissected tissue. Samples were loaded (20µg / lane) onto a 12% acrylamide gel alongside a protein ladder (Thermofisher, 26616) before being run at 60V for 35 minutes followed by 120V for 100 minutes. Wet transfer to a PVDF membrane was completed in 90 minutes using 400mA. The membrane was blocked for 2hrs in 5% non-fat dry milk before being incubated overnight at 4°C in HB7863 at a 1:10,000 dilution (0.1µg/ml) and HB9177 (anti-GAPDH monoclonal antibody) at a 1:2,000 dilution (0.5µg/ml). Following washing, the membrane was incubated in secondary antibody (1:10,000 dilution, Polyclonal goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated, Sigma Aldrich A3682) for 2hrs. For more detail please see our Western blotting protocol. Detection was accomplished using Clarity Western ECL substrate (BioRad, 1705061) and a Licor Odyssey Fc imaging system (ECL channel: 10 min exposure, 700nm channel: 30 sec exposure). |
![]()
|
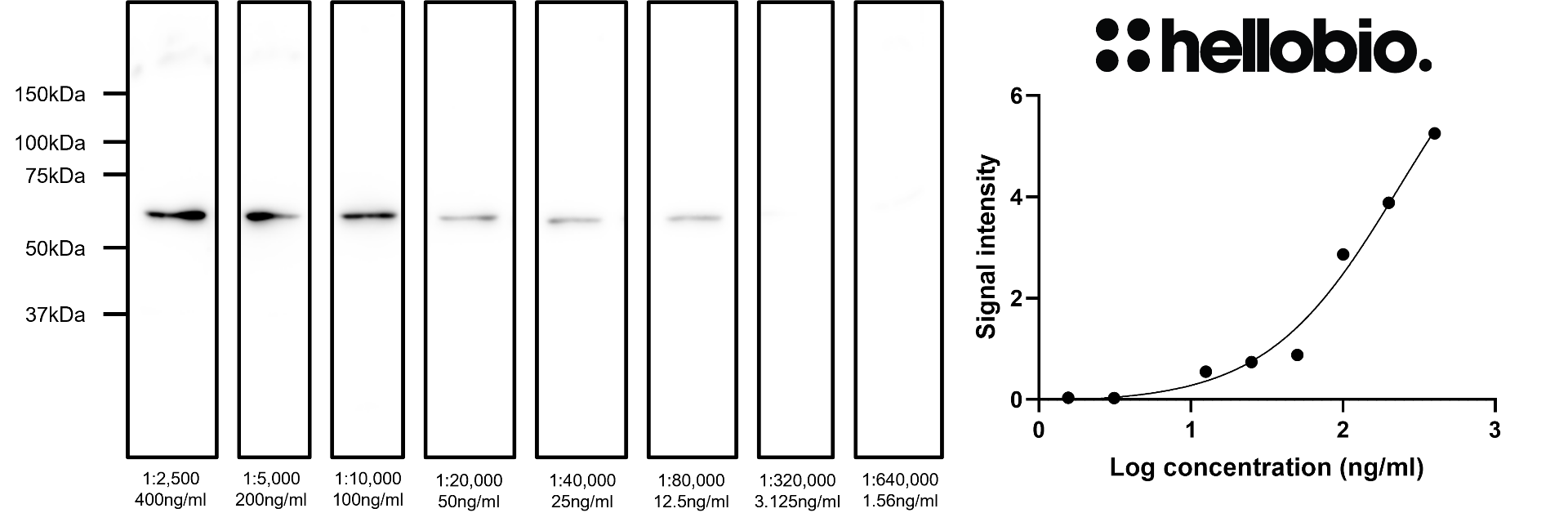
Figure 4. Concentration response of HB7863 staining in rat liver lysate. HB7863 shows consistent results with low background at dilutions as low as 1:80,000 (12.5 ng/ml). Method: Liver lysate was prepared from fresh rat livers following established protocols. Samples were loaded (20µg / lane) onto a 10% acrylamide gel alongside a protein ladder (Thermofisher, 26616) before being run at 60V for 30 minutes followed by 120V for 100 minutes. Wet transfer to a PVDF membrane was completed in 90 minutes using 400mA. Following transfer the membrane was cut into strips using Ponceau dye to visualise lanes. Strips were blocked for 2hrs in 5% non-fat dry milk before being incubated overnight at 4°C in HB7863. Each strip was incubated separately with a separate HB7863 concentration with this ranging from 400ng/ml (1:2,500 dilution) to 1.56ng/ml (1:640,000 dilution). Following washing, the membrane was incubated in secondary antibody (1:10,000 dilution, Polyclonal goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated, Sigma Aldrich A3682) for 2hrs. For more detail please see our Western blotting protocol. Detection was accomplished using Clarity Western ECL substrate (BioRad, 1705061) and a Licor Odyssey Fc imaging system (ECL channel: 10 min exposure, 700nm channel: 30 sec exposure). Band intensity was calculated using Image Studio version 5.2.5 (LiCor) and a graph was constructed in GraphPad Prism 9 using a 3-parameter Hill equation curve fit. |
![]()
|
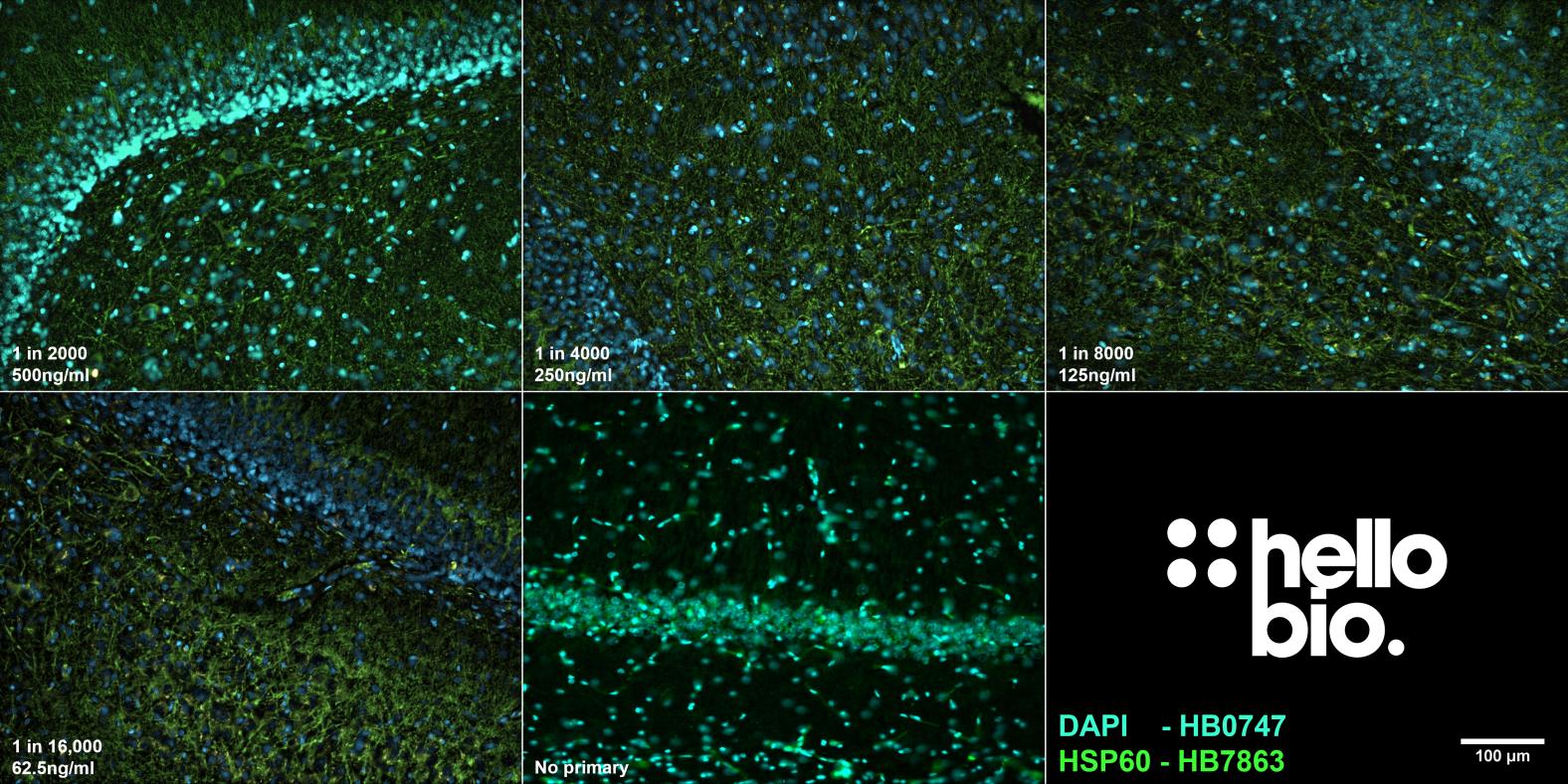
Figure 5. The effect of varying HB7863 concentration upon staining in rat dentate gyrus. HB7863 successfully labelled the dense network of fibres in the hilus of the dentate gyrus in 40µm rat hippocampal sections at a range of dilutions. Method: hippocampi were dissected from rat brains and fixed overnight in 4% PFA before then being incubated in 30% sucrose (in PBS) for another 24hrs. A freezing microtome was used to cut 40µm transverse slices before sections were incubated in 0.05M glycine for 30 minutes. Sections were blocked in 1% BSA, 22.52mg/ml glycine before incubation overnight in varying concentrations of HB7863 (1:2,000 to 1:16,000 dilutions, 62.5-500ng/ml). This was followed by a two hour incubation with secondary antibody (Polyclonal goat anti-mouse DyLight 488 conjugated, Thermofisher 35503, 1:300 dilution). DAPI (HB0747) was used at 1µg/ml to visualise cell nuclei. For more detail please see our IHC(IF) protocol. Images were captured using a Leica DM2500 epifluorescence microscope (20x objective) coupled to a Leica DFC7000T colour digital camera with DAPI and I3 filters. Exposure times were as follows:
1:2,000 – DAPI: 10x gain,15.6ms exposure; I3 10x gain, 40.0ms exposure
1:4,000 – DAPI: 10x gain, 12.4ms exposure; I3 10x gain, 53.1ms exposure
1:8,000 – DAPI: 10x gain, 9.2ms exposure; I3: 10x gain, 53.1ms exposure
1:16,000 – DAPI: 1x gain, 93.0ms exposure; I3: 1x gain, 808.0ms exposure
No primary – DAPI: 10.18ms exposure, I3: 112.ms exposure (taken using different microscope: Leica DMI6000B with Photometric-Prime95B camera).
Images were processed in ImageJ (Schindelin et al., 2012. Nat Methods, 9(7), 676–682) using the subtract background (50px rolling ball radius) tool before being stacked and made into a montage. |
![]()
|
Figure 6. GFP expression in transfected HEK293 cells with HSP60 and GAPDH loading controls (stripped and reprobed). HB7863 showed consistent staining across all HEK293 samples following stripping and reprobing of the membrane. Method: HEK293 cells were cultured and transfected following established protocols (Lee et al., 2019. PLoS ONE, 14(5):e0213116) with either pEGFP-C2 or pmCherry-C3 plasmids. After allowing 3 days for expression lysates were prepared and loaded (equal loading) onto a 15% acrylamide gel alongside a protein ladder (New England Biolabs, P7719S) before being run at 60V for 30 minutes followed by 120V for 100 minutes. Wet transfer to a PVDF membrane was completed in 90 minutes using 400mA. The membrane was blocked for 2hrs in 5% non-fat dry milk before being incubated overnight at 4°C in anti-GFP antibody (mouse monoclonal IgM) at a 1:8,000 dilution (0.125µg/ml). Following washing the membrane was incubated in secondary antibody (1:10,000 dilution, Polyclonal goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated, Sigma Aldrich A3682) for 2hrs. For more detail please see our Western blotting protocol. Detection was accomplished using Clarity Western ECL substrate (BioRad, 1705061) and a Licor Odyssey Fc imaging system (ECL channel: 10 min exposure, 700nm channel: 30 sec exposure). Following imaging the membrane was stripped with two changes of stripping buffer (15g/l glycine, 1g/l SDS, 1% Tween 20, pH2.2) before being washed, blocked for 1 hour in 5% non-fat dry milk and incubated in HB7863 (1:5,000 dilution, 0.2 µg/ml) and HB9177 (1:4,000 dilution, 0.25µg/ml) for 2 hours at room temperature. Following washing, the membrane was incubated in secondary antibody (1:10,000 dilution, Polyclonal goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated, Sigma Aldrich A3682) for 1 hour and visualised again using Clarity Western ECL substrate (BioRad, 1705061) and a Licor Odyssey Fc imaging system (ECL channel: 4 min exposure, 700nm channel: 30 sec exposure). |
![]()
|
Figure 7. HSP60 expression in various tissue lysates and preparations. HB7863 revealed a single band of size 58kDa present in all samples except the rat brain cytosol fractions. Method: mouse brain and rat brain membrane (P2) and cytosol fractions were prepared following previous work (Molnar et al., 1993. Neuroscience 53:307-326) from freshly collected adult brains. Other tissue lysates were prepared following established protocols from freshly dissected tissue. Samples were loaded (20µg / lane) onto a 12% acrylamide gel alongside a protein ladder (Thermofisher, 26616) before being run at 60V for 30 minutes followed by 120V for 100 minutes. Wet transfer to a PVDF membrane was completed in 100 minutes using 400mA. The membrane was blocked for 2hrs 20m in 5% non-fat dry milk before being incubated overnight at 4°C in HB7863 at a 1:10,000 dilution (0.1µg/ml). Following washing, the membrane was incubated in secondary antibody (1:10,000 dilution, Polyclonal goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated, Sigma Aldrich A3682) for 2hrs. For more detail please see our Western blotting protocol. Detection was accomplished using Clarity Western ECL substrate (BioRad, 1705061) and a Licor Odyssey Fc imaging system (ECL channel: 10 min exposure, 700nm channel: 30 sec exposure). |
![]()
|
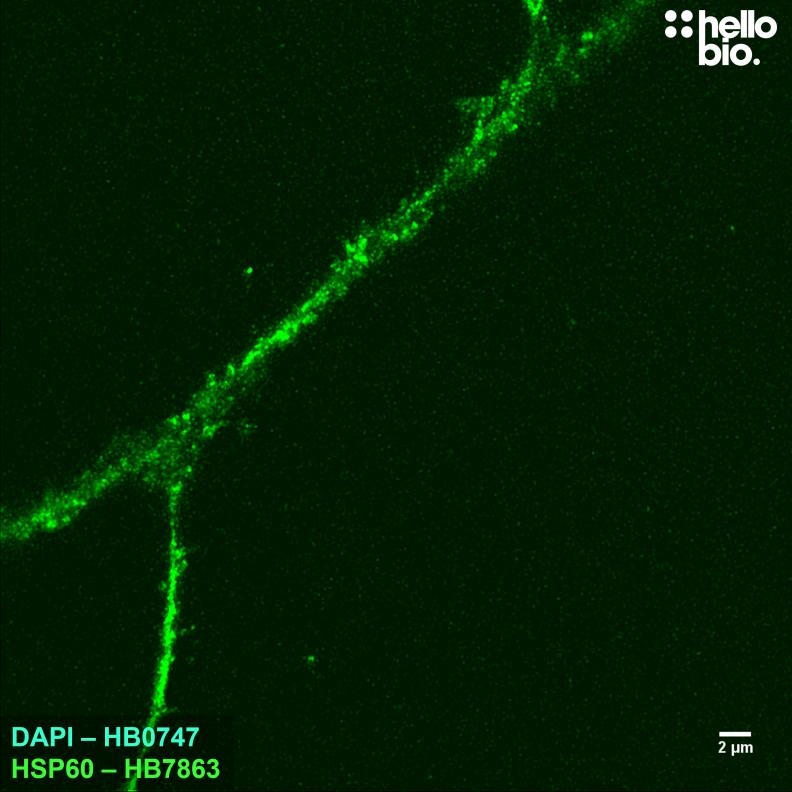
Figure 8. HSP60 staining with HB7863 reveals the network of mitochondria present within a neuron axon. Mitochondria are highly prevalent in neurones due to their high energy requirements; this was visualised using HB7863 in cultured rat neurones. Method: neurones were cultured from PND2 rats following established protocols (Brewer and Torricelli, 2007. Nat Protoc 2, 1490–1498) and fixed with 4% PFA on DIV21. Cells were permeabilised with 0.1% Triton X-100 followed by blocking in 1% BSA, 300mM glycine. HB67863 was incubated overnight (4°C) at a 1:1000 dilution (1µg/ml) followed by a one hour incubation with secondary antibody (Polyclonal goat anti-mouse DyLight 488 conjugated, Thermofisher 35503, 1:300 dilution). For more detail please see our ICC protocol. Images were captured using a Leica SPE confocal laser scanning microscope coupled to a Leica DMi8 inverted epifluorescence microscope. The image was captured using a 63x objective (3.5x zoom) and 488nm (43.5% power, gain: 658) laser line in a z-stack (0.18 µm spacing). Deconvolution was carried out using Huygens Essential (Scientific Volume Imagine) followed by the stack being flattened using a maximum Z projection in ImageJ (Schindelin et al., 2012. Nat Methods, 9(7), 676–682). |